Navigation API
The Navigation API allows for the manipulation of the navigation system used in Moodle.
What the navigation is
It's very important to understand what the navigation is exactly within Moodle. One of the goals for Moodle 2.0 was to standardise navigation throughout Moodle and try to bring order to the structure of a Moodle site. Navigation is available through the page object $PAGE, against which you set the heading for the page, the title, any JavaScript requirements, etc. The navigation structure uses the information $PAGE contains to generate a navigation structure for the site. The navigation or settings blocks are interpretations of the navigation structure Moodle creates.
This navigation structure is available through three variables:
$PAGE->navigation- The main navigation structure, it will contain items that will allow the user to browse to the other available pages$PAGE->settingsnav- The settings navigation structure contains items that will allow the user to edit settings$PAGE->navbar- A special structure for page breadcrumbs
A conceptual view of the information architecture that sits behind the navigation tree is here:
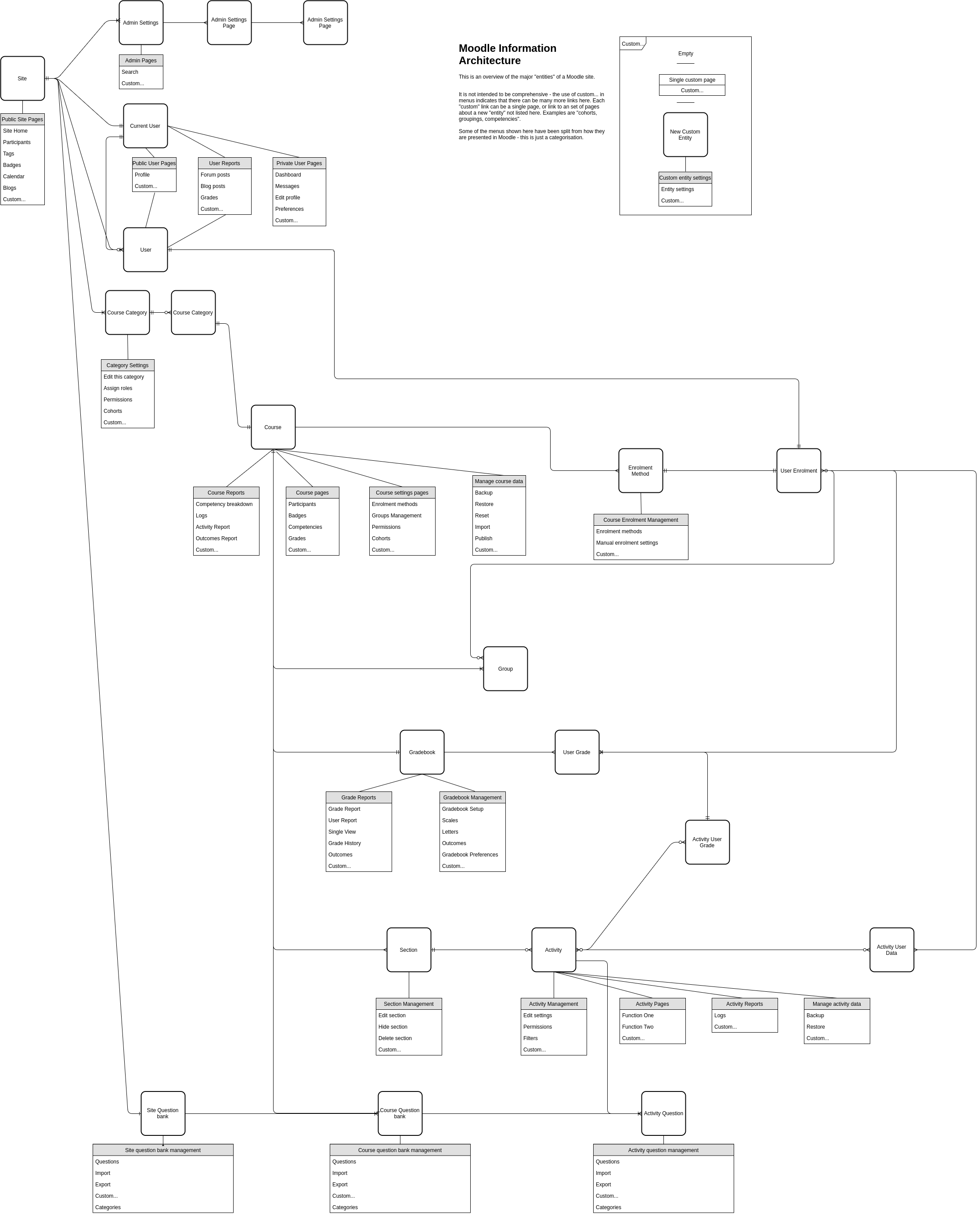
This diagram represents the major entities and how they are related to each other. Examples are given of the type of functions available on each kind of entity.
What the navigation is not
The navigation is NOT the navigation block or the settings block! These two blocks were created to display the navigation structure. The navigation block looks at $PAGE->navigation, and the settings block looks at $PAGE->settingsnav. Both blocks interpret their data into an HTML structure and render it.
- The navigation is a back-end structure that is built behind the scenes and has no immediate method of display.
- The navigation and settings blocks display the back-end navigation structure but add nothing to it at all.
In a model-view-controller pattern, $PAGE->navigation, $PAGE->settingsnav, and $PAGE->navbar are the models, and the blocks are views.
The navbar is just the path to the active navigation or settings item. The navbar is not displayed by a block; instead it is added into the theme's layout files and displayed by the core renderer.
How the navigation works
The main navigation structure can be accessed through $PAGE->navigation. The navigation and settings are contextual in that they will relate to the page that the user is viewing. This is determined by other $PAGE object properties:
$PAGE->contextis a Moodle context that immediately outlines the nature of the page the user is viewing.$PAGE->courseis the course the user is viewing. This is essential if the context is CONTEXT_COURSE or anything within it. However, it is also useful in other contexts such as CONTEXT_USER.$PAGE->cmis the course module instance. This is essential if the context is CONTEXT_MODULE.$PAGE->urlis used to match the active navigation item.
Nearly every page sets $PAGE->url through a call to $PAGE->set_url() however not many explicitly set the context, course, or cm. When you call require_login() with a course or context_module, it automatically calls the following:
if ($cm) {
$PAGE->set_cm($cm, $course); // sets up global $COURSE
} else {
$PAGE->set_course($course);// sets up global $COURSE
A page will only be required to explicitly set a context, course, or cm under one of these conditions:
require_loginis NOT being called correctly- The page is using CONTEXT_SYSTEM, CONTEXT_COURSECAT, or CONTEXT_USER (call
$PAGE->set_context()). - The page is using a course or cm but it is also using one of the above contexts (call
$PAGE->set_course()or$PAGE->set_cm()).
The navigation structure cannot be generated before the $PAGE object is configured. It is only generated when it is first used, either when something tries to access the structure or when code tries to add to it. The navigation is initialised in a specific order:
- Main navigation structure
- Settings navigation
- Navbar (does not need to be generated because of its simple contents and rendering)
Extending the navigation
Code extension
This method of extending is when the code arbitrarily extends the navigation during its execution. Extending the navigation through this means allows you to extend the navigation anywhere easily, however it will only be shown on pages where your extending code gets called (you should probably put it in a function within lib.php).
Navigation extensions that apply all the time (even when not on pages including your code) can be made by putting them in your plugin's settings.php file.
These examples are taken from the General Developer Forum: Moodle 2 - how to set up breadcrumbs for a module page. It has further information that is well worth reading.
Navigation
Extending the main navigation structure
$previewnode = $PAGE->navigation->add(
get_string('preview'),
new moodle_url('/a/link/if/you/want/one.php'),
navigation_node::TYPE_CONTAINER
);
$thingnode = $previewnode->add(
get_string('thingname'),
new moodle_url('/a/link/if/you/want/one.php')
);
$thingnode->make_active();
The above lines of code adds a preview node to the bottom of the navigation and then adds a thing node to the preview node (adding a leaf to our tree). The final line of code makes the thing node active so that the navbar finds it however if the URL you give it is the same as the url you set for the page it will automatically be marked active and you won't need this call.
Extending the navigation for the course
This example assumes that you already know the course ID and have already called require_login(). This loads the navigation data for the specified course.
$coursenode = $PAGE->navigation->find($courseid, navigation_node::TYPE_COURSE);
$thingnode = $coursenode->add(
get_string('thingname'),
new moodle_url('/a/link/if/you/want/one.php')
);
$thingnode->make_active();
The first line of this code finds the course node using a combination of the ID of the course, and the node type navigation_node::TYPE_COURSE.
This example relies on the navigation API to generate the navigation up to the course, and the example then adds to that structure.
Moodle loads plugins in alphabetical order. This means that plugin_b can find a node added by plugin_a but not the other way around. However, plugins must abide by the Component communication principles.
Settings navigation
Adding to the settings navigation is very similar to the general navigation, only using the settingsnav property of the $PAGE API.
$settingnode = $PAGE->settingsnav->add(
get_string('setting'),
new moodle_url('/a/link/if/you/want/one.php'),
navigation_node::TYPE_CONTAINER
);
$thingnode = $settingnode->add(
get_string('thingname'),
new moodle_url('/a/link/if/you/want/one.php')
);
$thingnode->make_active();
Add Settings folder to navigation
This example adds a settings folder to the navigation API at Site administration / Plugins / Activity modules / Assignment.
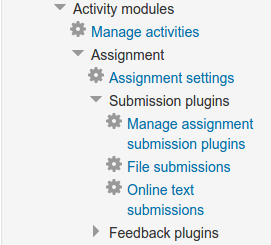
An example of adding a navigation folder to a settings.php for a block with a link to the settings page and a external page is bellow.
// Create a submenu in the block menu.
// This can be found in:
// - blocksettings for block plugins
// - modsettings for activity modules
// - localplugins for Local plugins
// The default menus are defined in admin/settings/plugins.php.
$ADMIN->add(
'blocksettings',
new admin_category(
'blocksamplefolder',
get_string('pluginname', 'mod_sample')
)
);
// Create settings block.
$settings = new admin_settingpage($section, get_string('settings', 'block_sample'));
if ($ADMIN->fulltree) {
$settings->add(
new admin_setting_configcheckbox(
'block_sample_checkbox',
get_string('checkbox', 'block_sample'),
get_string('checkboxdescription', 'block_kronoshtml'),
0
)
);
}
// This adds the settings link to the folder/submenu.
$ADMIN->add('blocksamplefolder', $settings);
// This adds a link to an external page.
$ADMIN->add(
'blocksamplefolder',
new admin_externalpage(
'block_sample_page',
get_string('externalpage', 'block_sample'),
"{$CFG->wwwroot}/blocks/sample/sample.php"
)
);
// Prevent Moodle from adding settings block in standard location.
$settings = null;
Navbar
The following example extends the navbar navigation.
$PAGE->navbar->ignore_active();
$PAGE->navbar->add(
get_string('preview'),
new moodle_url('/a/link/if/you/want/one.php')
);
$PAGE->navbar->add(
get_string('name of thing'),
new moodle_url('/a/link/if/you/want/one.php')
);
The above code tells the navbar to ignore the automatically detected active page and to instead use what is manually added, at which point we add two items as shown.
Plugin Callbacks
These are specific functions that the navigation looks for and calls if they exist for the plugin, presently only three plugin types can extend the navigation through these call-backs.
Ideally all entries in "Administration / Site administration" tree should be done via settings.php files but sometimes it may be easier to directly modify the navigation structure created from the admin settings tree (such as when adding links to external pages).
Module
Modules have two call-back methods, first to extend the navigation, and second to extend the settings. These call-backs get called when ever the user is viewing a page within the module and should only extend the navigation for the module.
function {modulename}_extend_navigation(
${modulename}node,
$course,
$module,
$cm
);
function {modulename}_extend_settings_navigation(
$settings,
${modulename}node
);
You may be required to add a node in a specified order within the menu navigation menus. To do this you need to examine the node object as given in the respective parameters in the functions above, then find the key of the child node you wish to place the link before. For example, applying the code below will put a direct link to grade report.
function my_plugin_extend_settings_navigation($settingsnav, $context){
$addnode = $context->contextlevel === 50;
$addnode = $addnode && has_capability('gradereport/grader:view', $context);
if ($addnode) {
$id = $context->instanceid;
$urltext = get_string('gradereportlink', 'myplugin');
$url = new moodle_url('/grade/report/grader/index.php',[
'id' => $id,
]);
// Find the course settings node using the 'courseadmin' key.
$coursesettingsnode = $settingsnav->find('courseadmin', null);
$node = $coursesettingsnode->create(
$urltext,
$url,
navigation_node::NODETYPE_LEAF,
null,
'gradebook',
new pix_icon('i/report', 'grades')
);
// Add the new node _before_ the 'gradebooksetup' node.
$coursesettingsnode->add_node($node, 'gradebooksetup');
}
// ...
}
Course Formats
Course formats are able to completely redefine the way in which navigation is generated for a course, as well as this they also have several methods to ensure the navigation is generated correctly.
Course Reports
By default reports don't add themselves or anything else to the navigation however there is a call-back that can be implemented to allow them to do so.
Local Plugins
Local plugins have two call-back methods, first to extend the navigation, and second to extend the settings.
function local_{pluginname}_extend_navigation(
global_navigation $nav
);
function local_{pluginname}_extend_settings_navigation(
settings_navigation $nav,
context $context
);
Course settings
Any plugin implementing the following callback in lib.php can extend the course settings navigation.
function <component>_extend_navigation_course(
navigation_node $parentnode,
stdClass $course,
context_course $context
);
User settings
Any plugin implementing the following callback in lib.php can extend the user settings navigation.
function <component>_extend_navigation_user_settings(
navigation_node $parentnode,
stdClass $user,
context_user $context,
stdClass $course,
context_course $coursecontext
);
Category settings
Any plugin implementing the following callback in lib.php can extend the category settings navigation.
function <component>_extend_navigation_category_settings(
navigation_node $parentnode,
context_coursecat $context
);
Frontpage settings
Any plugin implementing the following callback in lib.php can extend the frontpage settings navigation.
function <component>_extend_navigation_frontpage(
navigation_node $parentnode,
stdClass $course,
context_course $context
);
User profile
Any plugin implementing the following callback in lib.php can extend the user profile navigation.
function <component>_extend_navigation_user(
navigation_node $parentnode,
stdClass $user,
context_user $context,
stdClass $course,
context_course $coursecontext
);
Boost theme
The navigation API is specifically about allowing the manipulation of nodes in an in-memory tree structure that is used as the basis of building navigation components in the page. The navigation and settings blocks are 2 examples of such components and the flat navigation and settings menus in the Boost theme are another example. The navigation component itself can decide to show all or only part of the navigation tree in order to not overwhelm the user viewing the page. Whether a node is actually displayed depends on where in the tree the node was added, what is the current page in the navigation tree, and the specific navigation components that are used to provide navigation functionality in the current theme.
If you are testing in the Boost theme - all nodes that are added to settings tree are displayed in the course or activity settings menu. This is shown as a cog on the front page of the course or activity.
Only the most important pre-selected nodes are displayed in the flat-navigation drawer in order to provide consistency and avoid overwhelming the user with too many links.
It is possible, but not recommended, for plugins to add nodes to the flat navigation (see FAQ's and troubleshooting for more information).
FAQ's and troubleshooting
Q. My page is on the navigation but it doesn't find it?
The first thing to do here is check the URL you are setting for the page. It should match the URL your page has within the navigation. If it doesn't you have two options, first change your $PAGE->set_url() call, or second override the URL the navigation is using to find the active node as shown below:
navigation_node::override_active_url(
new moodle_url('/your/url/here.php', [
'param' => 'value',
])
);
Q. How do I add a node to the "flat" navigation in the Boost theme?
Adding a node to the "flat" navigation is only possible for Moodle versions before 4.0. After creating a node and adding it to the navigation tree - you can set the property showinflatnavigation to true in order for this node to be displayed in the flat navigation.
$node = navigation_node::create(...);
$node->showinflatnavigation = true;
$navigation->add_node($node);
This is highly discouraged because the number of nodes in this flat navigation has been deliberately restricted to a very small number of the most important links that are applicable to all user roles.
Adding more links to this menu will make it harder to use, inconsistent for different users, and inconsistent for different sites.
Consider carefully if you really need to fill an additional 230x44 pixels of every single page in Moodle for every single user with a link to your thing. There are many other places to include links to your thing and most are automatically built from the navigation tree without forcing nodes to display in the flat navigation. For example, in the settings menu of a course, profile page, preferences page, reports, and so on.